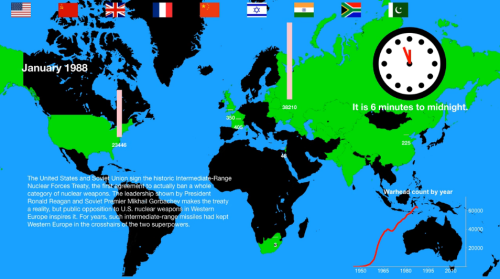
Circa 1988: the Doomsday Clock during safer times. (Courtesy: The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists)
By Hamish Johnston
This year marks the 70th anniversary of the Doomsday Clock that is produced by The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. Currently at two and a half minutes to midnight, the clock represents the likelihood of a human-caused global catastrophe. Originally, it focused exclusively on a nuclear Armageddon, but in 2007 climate change and other technologically-driven processes were added to the mix. The clock was initially set at seven minutes to midnight in 1947 and the Bulletin has produced a video that charts the ups and downs over the past seven decades. Is there any good news? In the image above you can see that South Africa was a nuclear power in 1988, and it has since disarmed.
What could humanity do when faced with the imminent destruction of our planet? One solution – at least according to Stephen Hawking, Neil Young and others – is to decamp to another world. And why not one that resembles the fictional planet that harbours the continents of Westeros and Essos in Game of Thrones? An important feature of the world created by George R R Martin is that the length and onset of seasons is variable and unpredictable. Now, astrophysicist Ethan Siegel argues that such a planet could be out there somewhere in the cosmos. See “Game of Thrones home world could actually exist, says science” for more details.
Guidelines
Show/hide formatting guidelines
this text was deletedwhere people live in harmony with nature and animals</q>
Some text